Next | Prev | Up | Top | Contents | Index
EISA Product Identifier
EISA expansion boards, embedded devices, and system boards have a four-byte product identifier (ID) that can be read from I/O port addresses 0xsC80 through 0xsC83 in the card's I/O address space, where s is the offset of the card slot. For example, the slot 1 product ID can be read as a 4-byte value from I/O port addresses 0x1C80. This value can be tested in an exprobe parameter of the VECTOR line during system boot (see "Configuring IRIX").
The first two bytes (0xsC80 and 0xsC81) contain a compressed representation of the manufacturer code. The manufacturer code is a three-character code (uppercase ASCII characters in the range of A to Z) chosen by the manufacturer and registered with the standard (see "Standards Documents" on page xxxviii). The manufacturer code "ISA" is used to indicate a generic ISA adapter.
The three-character manufacturer code is compressed into three 5-bit values so that it can be incorporated into the two I/O bytes at 0xsC80 and 0xsC81. The compression procedure is as follows:
- Find the hexadecimal ASCII value for each letter:
ASCII for "A"-"Z" : "A" = 0x41, "Z" = 0x5a
- Subtract 0x40 from each ASCII value:
Compressed "A" = 0x41-0x40 = 0x01 = 0000 0001
Compressed "Z" = 0x5a-0x40 = 0x1A = 0001 1010
- Discard leading 0-bits, retaining the five least significant bits of each letter:
Compressed "A" = 00001. Compressed "Z" = 11010
- Compressed code = concatenate "0" and the three 5-bit values:
"AZA" = 0 00001 11010 00001
Figure 17-2 summarizes the contents of the EISA manufacturer ID value.
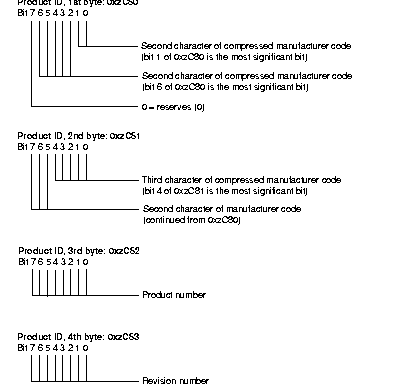
Figure 17-2 : Encoding of the EISA Manufacturer ID
Next | Prev | Up | Top | Contents | Index

